Remote sensing and reanalysis are two main approaches for estimating large-scale precipitation information. However, these products typically contain substantial uncertainties. Although data merging can significantly suppress precipitation uncertainty, current merging frameworks highly relies on ground measurements and are only applicable to independent products.
Prof. Jianzhi Dong of our department recently developed a new global precipitation merging framework: Statistical Uncertainty analysis-based Precipitation mERging framework (SUPER). This framework mathematically solves the random error variance, rain/no-rain error and inter-product error covariances of different precipitation products. The error information is used to estimate the optimal merging weight of each product. The SUPER framework also embeds an “adaptive” algorithm which can automatically exclude precipitation products destabilizing the merging results.
The SUPER framework has been applied to merging seven commonly used precipitation products. Ground-based validation suggests that SUPER outperforms current state-of-the-art precipitation products (Figures 1 and 2).
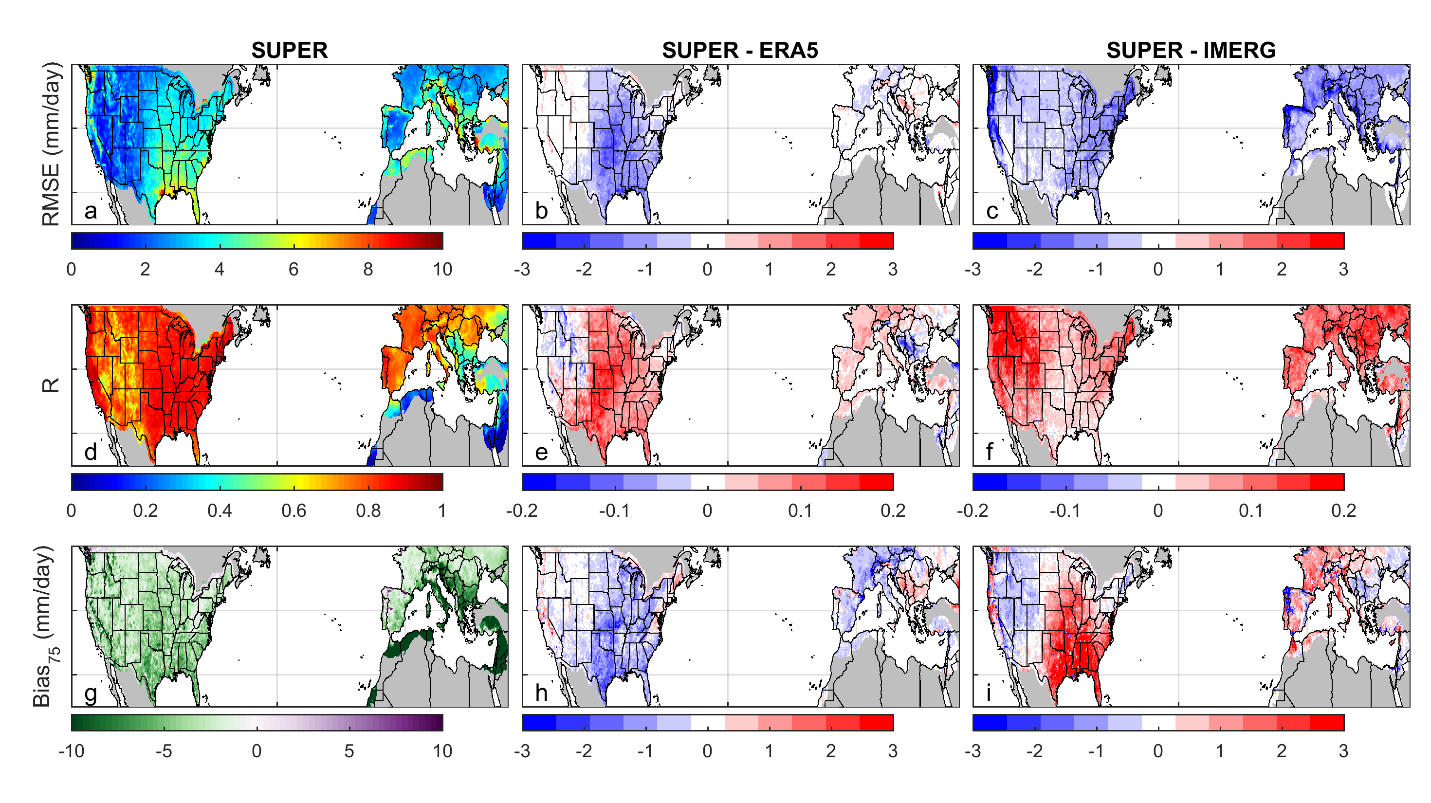
Figure 1. The accuracy of SUPER and its performance relative to ERA5 and IMERG precipitation products.
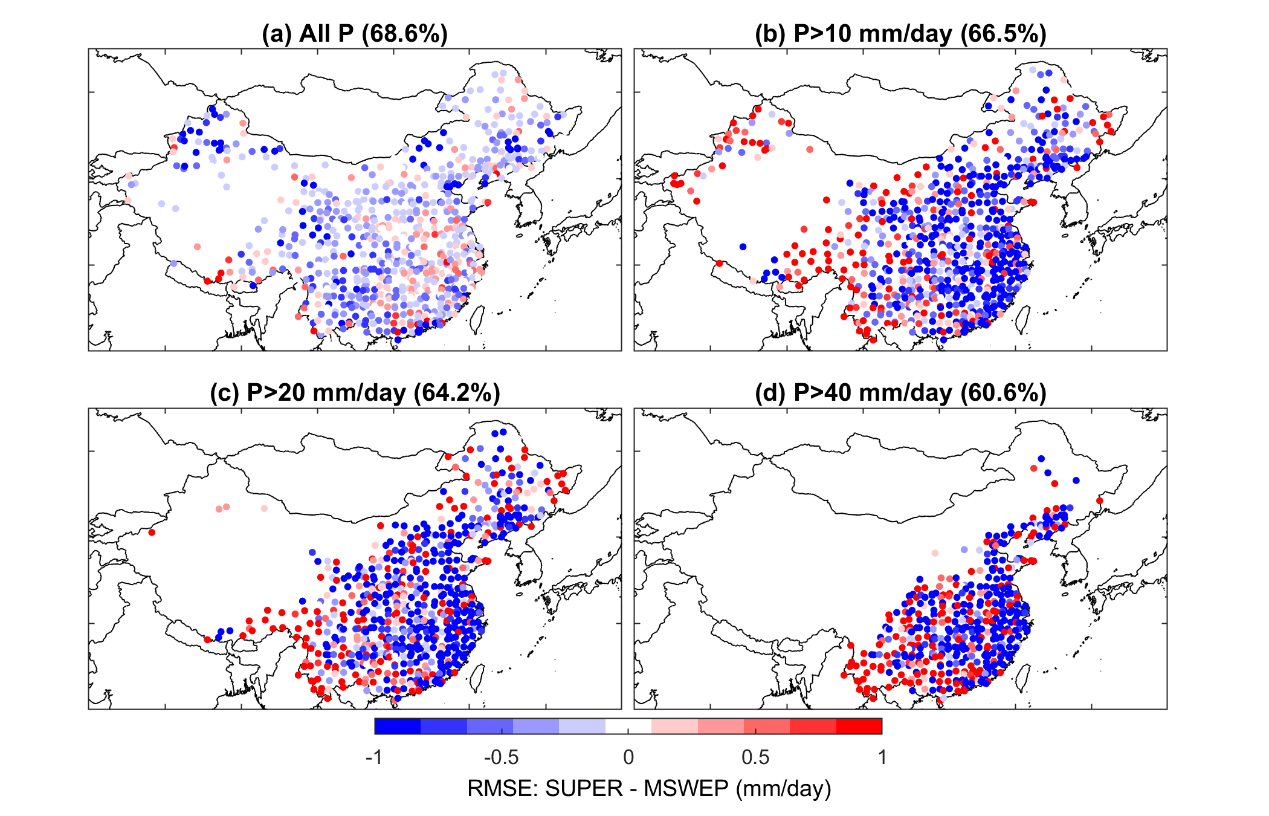
Figure 2. Comparison of SUPER and MSWEP. Blue dots represent the meteorological stations that suggest SUPER outperforms MSWEP.
This research is published on “Remote Sensing of Environment”, which is a top remote sensing journal (IF = 13.85). The first and the corresponding author of this study is Professor Jianzhi Dong from Institute of Surface-Earth System Science at Tianjin University. This work is collaborated with Dr. Wade Crow (USDA-ARS-HRSL), Prof. Xi Chen (Tianjin University) and other international experts in large-scale hydrology. This study is supported by National Science Foundation of China (52179021, 51909121, U21A2004, 42075189).
References:
Dong, J., Crow, W. T., Chen, X., Tangdamrongsub, N., Gao, M., Sun, S., Qiu, J., Wei, L., Gao, H., & Duan, Z. (2022). Statistical uncertainty analysis-based precipitation merging (SUPER): A new framework for improved global precipitation estimation. Remote Sensing of Environment, 283, 113299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2022.113299
Dong, J., Crow, W.T., Duan, Z., Wei, L., & Lu, Y. (2019). A double instrumental variable method for geophysical product error estimation. Remote Sensing of Environment, 225, 217-228
Dong, J., Crow, W.T., & Reichle, R. (2020). Improving rain/no-rain detection skill by merging precipitation estimates from different sources. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 21, 2419-2429
Dong, J., Lei, F., & Wei, L. (2020). Triple collocation based multi-source precipitation merging. Frontiers in Water 2: 1. doi: 10.3389/frwa
Dong, J., Wei, L., Chen, X., Duan, Z., & Lu, Y. (2020). An instrument variable based algorithm for estimating cross-correlated hydrological remote sensing errors. Journal of Hydrology, 581, 124413