Organosulfates(OSs) are important tracers of atmospheric physical and chemical processes. OSs generally refer to ester compounds and their derivatives containing sulfate. It is the most important organic sulfur(OS) compound in terrestrial atmospheric particulate matter, and its content can account for up to 30% of organic aerosol content and 10% of total sulfate content, making a significant contribution to PM2.5 content. The discovery of OSs not only enriches the generation pathway of secondary organic aerosol(SOA), but also provides insights to understand the generation of biogenic SOA(BSOA) under anthropogenic influence. The total analysis of OSs is combined with typical OSs, and the spatio-temporal distribution characteristics and formation mechanism of OSs are deeply analyzed.
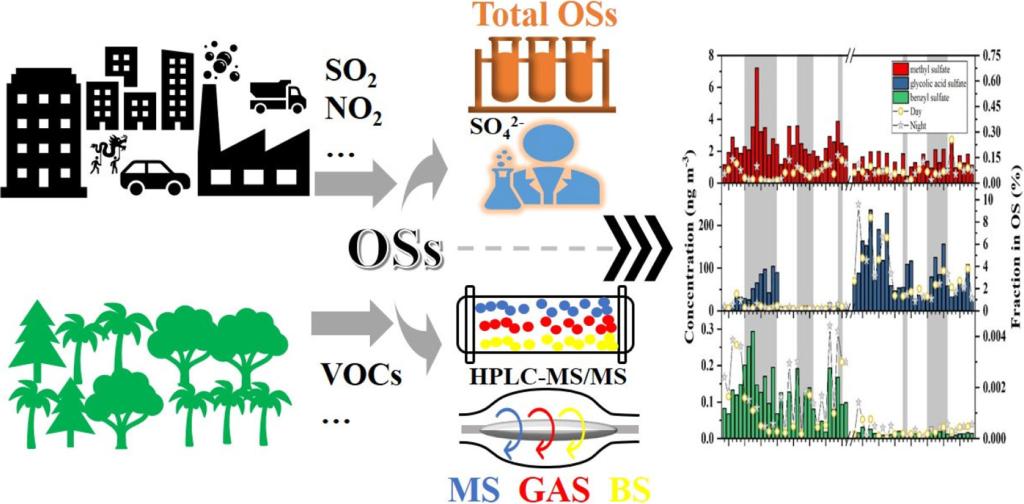
To understand their seasonal and diurnal distribution characteristics and formation mechanism in northern China, PM2.5 samples collected in daytime and nighttime in winter and summer 2019 in Tianjin, China were studied for total OSs and three OS species (methyl sulfate(MS), glycolic acid sulfate(GAS), benzyl sulfate(BS)). The S contents of total OSs(SOSs) in winter and summer were 0.6 ± 1 μg m−3 and 0.4 ± 0.3 μg m−3, respectively, in PM2.5. BS was less abundant among the measured species, and accounted for only 0.8%–4.8% of methyl sulfate(MS), and 0.01%–0.3% of glycolic acid sulfate(GAS). Average content of GAS was higher in summer than in winter, while that of MS and BS were opposite. The fractions of MS, GAS, and BS in SOSs were higher in daytime than that in night during winter, despite their concentrations were higher in nighttime, indicating that the concentrations of unidentified OS species were much higher in nighttime than in daytime. Such diurnal variations implied that relative humidity(RH) played a major role in the formation processes of OSs, especially biogenic OSs and the acid catalyzed reaction of SO42− might be a main pathway of OSs formation during winter. High T, RH and O3 determined biological GAS in summer, while NO2 and SO2 determined anthropogenic OSs in winter. We also found that the fractions of SOSs in S contents of organic sulfur(SOS) and the S contents of MS + GAS+BS (SMS+GAS+BS) in SOSs were accounted for only less than 10% and 5%, respectively. Therefore, this study suggests the components of OS and OSs in PM2.5 have not been discovered fully yet and need further research.
Article information: Ding, S., Chen, Y., Devineni, S.R., Pavuluri, C.M. and Li, X.-D. (2022) Distribution characteristics of organosulfates (OSs) in PM2.5 in Tianjin, Northern China: Quantitative analysis of total and three OS species. Science of the Total Environment 834, 155314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155314.