Carbon (C) occlusion within phytoliths (PhytOC) has a significant potential for long-term C sequestration in forest ecosystems. To unravel the role of forest composition on phytolith production, soil phytolith distribution, and phytolith C sequestration in soils, we investigated community composition and examinedphytoliths and PhytOC of mature leaves or needles of dominant trees and understory herbs, as well as soil profiles (50 cm depth) within Quercus, Betula, Larix and Pinus forest ecosystems of northern China. Results showed that herb layers contributed 72%, 52%, 40%, and 5% to the flux of phytolith production within Betula forest (18.0±1.26 kg ha–1 yr–1), Quercus forest (28.5±0.77 kg ha–1 yr–1), Larix forest (37.7±1.80 kg ha–1 yr–1) and Pinus forest (16.9±0.30 kg ha–1 yr–1), respectively.The distribution pattern of soil phytoliths from topsoil to subsoil could be classified into three types: significantly decreasing pattern (Betula forest and Quercus forest), non-significantly decreasing pattern (Larix forest), and initially increasing and then decreasing pattern (Pinus forest). Within 0-50 cm soil depth, the PhytOC storage of Betula forest, Quercus forest, Larix forest and Pinus forest were 0.29±0.02 t ha–1, 0.67±0.03 t ha–1, 0.46±0.03 t ha–1 and 0.37±0.02 t ha–1, respectively. Moreover, the soil PhytOC turnover times of these four forest types were estimated to be 537,503,363 and 560 year, respectively, which were at least 8-20 times slower than soil organic carbon contributing to climate change mitigation. Overall, our findings indicate that composition of the forest community controls the production flux of phytoliths and the distribution of soil phytoliths, and influences the biogenic silica and its coupled carbon cycles.
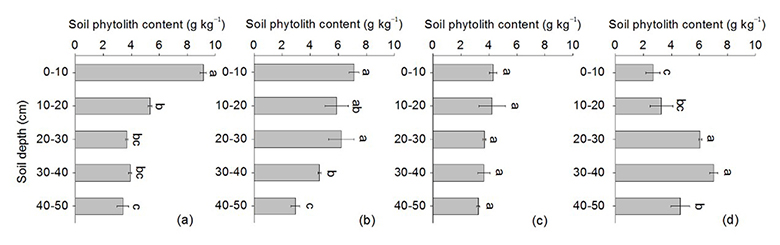
Fig. Phytolith variation from topsoil to subsoil in Betula forest (a), Quercus forest (b), Larix forest (c), and Pinus forest (d).
This work supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41522207, 41571130042) and the State's Key Project of Research and Development Plan of China (2016YFA0601002).
Article information: Xiaomin Yang, Zhaoliang Song, Hongyan Liu, Lukas Van Zwieten, Alin Song, Zimin Li, Qian Hao, Xiaodong Zhang, Hailong Wang. Phytolith accumulation in broadleaf and conifer forests of northern China: Implications for phytolith carbon sequestration. Geoderma, 2018, 312: 36–44.
Full text link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.10.005